2025 Tech Trends: Navigating the Future with ATP Gov
Cybersecurity in 2025: Securing Federal Networks with Next-Gen Strategies

Author: Eric Monterastelli
Cybersecurity in 2025: Securing Federal Networks with Next-Gen Strategies
As cyber threats become more sophisticated each day, the Federal Government continues prioritizing cybersecurity as a national security imperative. Agencies are adopting cutting-edge frameworks and technologies to safeguard sensitive systems. In 2025, the primary focus remains: Zero Trust Architecture, DevSecOps, Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR), saddled with Vulnerability and Threat Management. Through partnerships with leading OEMs and software companies, ATP Gov is focused on supporting Federal initiatives to enhance the cybersecurity readiness of our customers and partners.

Zero Trust Architecture and Vulnerability Management (VATP)
Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) has become a cornerstone of Federal cybersecurity policies since Cybersecurity Executive Order 14028. ZTA eliminates implicit trust, requiring continuous validation of all users, devices, and applications seeking network access. It’s a complex architecture that requires many technologies to adequately satisfy the nine pillars of the ZTA framework.
ATP Gov partners with companies like ZScaler, Fortinet, Broadcom, CISCO, CyberArk, Dynatrace, and other leaders in Zero Trust solutions to provide Federal agencies with identity-based access controls, real-time monitoring, advanced encryption capabilities, and more. ATP Gov’s robust solution stacks help reduce attack surfaces, thwart insider threats, and protect critical systems, aligning seamlessly with Federal Zero Trust mandates.
DevSecOps: Enhancing Cybersecurity with Vulnerability Management (VATP)
The transition to agile software development practices has driven the adoption of DevSecOps, which integrates security directly into the software development lifecycle. As part of a modern CI/CD (Continuous Improvement/Continuous Development) pipeline, this approach ensures that Federal systems are secure from the start, adhering to initiatives like the DHS’s CDM program.
ATP Gov collaborates with a plethora of technologies to ensure DevSecOps success, such as Red Hat, Atlassian, GitLab, Micro Focus, and Rancher Government Solutions, to name a few, which support the deployment of DevSecOps policies across Federal agencies. Combining these technologies enables automated security checks, continuous monitoring, and enhanced collaboration among development, security, and operations teams, ensuring that security is not an afterthought but a built-in process.
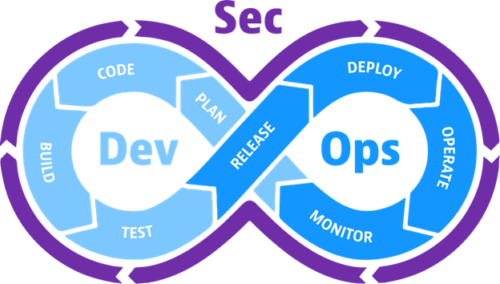
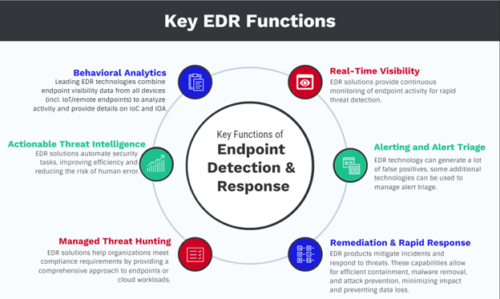
Despite some return-to-work initiatives bringing employees back to brick-and-mortar offices daily, Federal agencies continue to embrace telework and mobile-first strategies. Securing endpoints has become a priority, and Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) technologies provide real-time detection, investigation, and response capabilities to counter endpoint-specific threats.
ATP Gov’s partnerships with OEMs like CrowdStrike, EverFox, ExtraHop, ForeScout, Juniper, Trellix, and other leading endpoint security technologies empower agencies with cutting-edge tools to protect devices across distributed environments. These solutions offer rapid threat detection, forensic analysis, and automated response capabilities, all while safeguarding Federal networks from expanding and unforeseen attack surfaces.
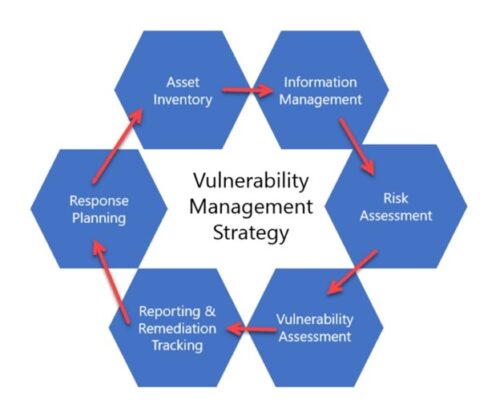
The Importance of Vulnerability Management (VATP) in Federal Cybersecurity
Meanwhile, FedRAMP continues to underscore the need for robust Vulnerability and Threat Management, particularly as agencies expand their reliance on cloud-based services. Proactively identifying and mitigating vulnerabilities is essential to reducing exposure to cyberattacks.
Through partnerships with Tenable, Menlo Security, Crowdstrike, and companies like Palo Alto Networks, ATP Gov provides comprehensive vulnerability management and mitigation solutions. We aim to deliver continuous monitoring, actionable threat intelligence, and compliance with Federal standards, ensuring agencies can find and address vulnerabilities before adversaries exploit them.
Supporting Federal Cybersecurity Objectives with Vulnerability Management (VATP)
ATP Gov’s collaboration with its extensive network of cyber security practitioners and technology partners ensures Federal agencies can access tailored solutions that meet their unique security requirements. Focusing on cybersecurity with a combined lens of Zero Trust (ZTA), DevSecOps, Endpoint (EDR), and Vulnerability/Threat Management, ATP Gov empowers its customers to build resilient defenses, protect critical infrastructure, and stay ahead of adversaries in an ever-evolving cyber landscape.
Our goal is to remain vigilant as cyber initiatives expand in 2025 with fresh solutions, frameworks, software, and technologies. By staying apprised of these changes, we aim to leverage the most innovative technologies and best practices, taking proactive steps to fortify the nation’s digital future.


